Datacenter vs Virtual Machines: How do they work?
Modern companies use computers in almost all aspects of doing business—communication, information storage, accounting, and day-to-day business functions. This includes data centers and virtual machines.
A data center is a centralized physical facility where corporate computers, networks, storage, and other IT equipment that support business operations live. The computers in a data center contain or facilitate business-critical applications, services, and data. Windows Server Datacenter is often seen as the ultimate powerhouse for high-level computing, with its wide array of features and functionality that make handling high levels easier.
But are data centers the same as virtual machines? What is their difference? How do they work?
This guide looks at the difference between data centers and virtual machines and how they work.

Jump to Section:
- Two Rules of Data centers and Virtual Machines
- What is a virtual machine?
- What is Virtualization
- How Virtualization Works
- Types of Hypervisors
- How is a virtual machine different from an actual physical machine?
- What is a VM datacenter?
- When would you need a virtual machine
- How to Choose a Virtual Machine Provider?
Two Rules of Data centers and Virtual Machines
Here are two important rules of setting up or using data centers and virtual machines:
Rule 1 - The Datacenter OS has to be the host machine.
Setting the foundation for your virtual machines is important in order to adhere to the licensing policy. As far as the host, there are a few different ways to set Datacenter as the primary instance, whether it be on a physical server, VMware cluster, or a Citrix XenServer. You can use any of the aforementioned methods to get your host up and running.
Rule 2 - The Virtual Machines must be rooted in Datacenter via Hyper-V.
To get these VM's up and running, you will need to complete activation through AVMA (Automatic Virtual Machine Activation) - a service built into Datacenter 2012 and all later editions. A virtual machine is automatically activated using an AVMA license, as long as the virtual machine is rooted in a licensed copy of Datacenter through Hyper-V.
What is a virtual machine?
A virtual machine is a computer file, typically known as an image, which is a replica of an actual machine. It is created within a computing environment known as the host. With a virtual machine, you are creating a computer within a computer.
We can also define virtual machines as software computers that provide the same functionality as physical computers. Just like physical machines, virtual machines run applications and an operating system.
Virtual machines are developed to perform specific tasks that are risky to perform in a host machine. They may be tasks such as accessing virus-infected data or testing operating systems. Virtual machines can also be fundamental in serving purposes such as server virtualization.
What is Virtualization
Before we can get deeper into data centers and virtual machines, we must understand what virtualization is.
Virtualization makes it possible to create multiple virtual machines, where each of these machines has its operating system and applications on a single physical device.
A virtual machine can’t interact directly with a physical computer. To operate, it needs a lightweight software layer known as a hypervisor, which coordinates between it and underlying physical hardware.
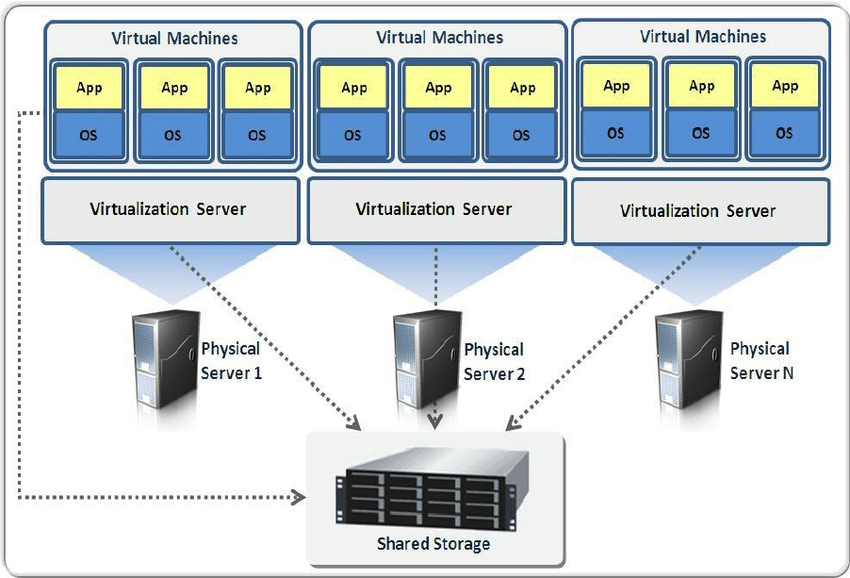
The work of the hypervisor is to allocate physical computing resources – such as memory, processors, storage, etc., to each virtual machine. It keeps VMs separate so that they don’t interfere with each other.
How Virtualization Works
When a hypervisor is used in a physical computer or server. It facilitates the physical computer to separate its operating system and applications from its hardware. It then divides itself into several independent virtual machines.
Each of these virtual machines can run its own operating systems and applications independently, while still sharing the primary resources from the bare metal server, which is managed by hypervisor. We are talking about resources such as memory, RAM, storage, and the rest.
The hypervisor will act to direct and allocate bare metal resources to each of the various new virtual machines, thus ensuring they don’t disrupt each other.
Types of Hypervisors
There are two primary types of hypervisors;
Type 1 Hypervisor
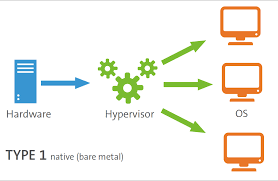
These types of hypervisors run directly on the physical hardware – which is usually a server and take the place of the operating system. Typically, they use a separate software product to create and manipulate the VMs on the hypervisor.
You can use the VM as a template for others, and duplicate it to create new ones. This will be mostly dependent on your needs. You might need to create multiple VM templates for different purposes, such as software testing, production databases, and development environments.
Type 2 Hypervisor
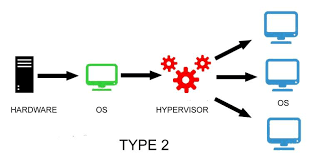
These types of hypervisors run as an application within a host. They usually target single-user desktop or notebook platforms. With type 2 hypervisors, you will manually create a VM and then install a guest OS in it.
You can then use the hypervisor to allocate physical resources to your VM. Doing this will require you to manually set the number of processor cores and memory it can use.
Types of Virtual Machines
There are different types of virtual machines. Common ones include Windows virtual machines, Android virtual machines, Mac virtual machines, iOS virtual machines, Java virtual machines, Python virtual machines, Linux virtual machines, VMWare virtual machines, and Ubuntu virtual machines.
Since they are many, let us discuss two only;
Windows Virtual Machine
Most hypervisors support VMs running the Windows OS as a guest. Microsoft’s Hyper –V hypervisor comes as part of the Windows operating system.
When you install it, it will create a parent partition that contains both itself and the primary Windows OS. Each of these gets privileged access to the hardware.
Other operating systems, including Windows guests, run in the child partition, which communicates with the hardware through the parent partition.
VMware virtual machines
VMware was an early virtualization software vendor. Today, it is a popular provider of both type 1 and 2 hypervisor and VM software to enterprise customers.
Running Multiple Virtual Machines
Multiple virtual machines can simultaneously run on the same physical computer. For servers, various operating systems run side by side, using a piece of software called a hypervisor, which is used to manage them.
Each virtual machine has its virtual hardware, including memory, CPUs, network interfaces, hard drives, and other devices. The virtual hardware is mapped to the real hardware on the physical machine.
Doing so saves costs by reducing the need for physical hardware systems along with associated maintenance costs that go with it.
How is a virtual machine different from an actual physical machine?
Choosing a virtual machine over a physical device – also known as a bare-metal server is less about competing capabilities, and more to do with knowing what you need and when you need it.
Physical machines are all about raw hardware, power, and isolation. They are single-tenant, physical servers completely void of hypervisor cycles (virtualization software), and entirely dedicated to a single customer – who is you!
There are those workloads that highly put a lot of priority on performance and seclusion, such as data-driven intensive applications and regulatory compliance mandates. These are typically best suited for physical servers- especially when deployed over sustained periods.
Ecommerce, CRM, ERP, SCM, and financial services applications are just a few workloads ideal for bare metal servers.
So you would need to place a hypervisor on top of the bare metal hardware to make a virtual machine when your workloads demand maximum flexibility and scalability.
Virtual machines seamlessly drive up server capacity and increase utilization – It becomes so ideal for moving data from one virtual machine to another, for resizing data sets and driving dynamic workloads.
What is a VM datacenter?
A virtual data center is a pool or collection of cloud infrastructure resources that are specially designed for enterprise business needs.
The basic resources are;
- Central Processing Unit
- Memory (RAM)
- Storage (Disk Space)
- Networking (bandwidth)
It is a virtual representation of a physical data center that is complete with servers, lots of networking components, storage clusters, all of which reside in a virtual space that is hosted by one or more actual data centers.
A virtual data center is a container for all inventory objects that are required to complete a functional environment for operating virtual machines. You can create multiple data centers or organize sets of environments.
One of the most significant benefits of cloud computing is to allow relatively small organizations to access IT infrastructure in terms of a virtual data center, without spending millions of dollars to construct an actual data center.
They will only need to pay for the resources that they use, and this allows for great flexibility and scalability. A virtual data center is a product of the Infrastructure as a service delivery model of cloud computing.
It can be used to provide on-demand computing, storage, and networking, as well as applications that are seamlessly integrated into an organization's existing IT infrastructure.
The main aim of having a data center is to allow organizations to add capacity or install new infrastructure, without the need to buy or install costly hardware, which would otherwise require additional workforce, space as well as power. The whole data center is provided over the cloud.
When would you need a virtual machine
Virtual machines have several uses. Many instances would require the use of a virtual machine, either for enterprise IT administration or other purposes. Here are a few options;
- Cloud Computing: For the last 10 years, VMs have been an integral part of cloud computing. They enable dozens of different types of applications and workloads to run and scale seamlessly.
- Support DevOps: If you have an enterprise team of developers, VMs offer great support to them. DevOps configure VM templates when testing their software development processes. They can create VMs for specific tasks, such as static software tests, automated development workflow, among others.
- Testing new operating systems: A VM will let you test-drive a new operating system in your desktop without affecting the primary default functions of your operating system.
- Investigating Malware: Virtual machines come in handy when it comes to malware research. They are used by software engineers and researchers testing malicious programs.
- Running incompatible software: Some users may prefer one operating system while still needing a program that is only available in another. Let’s take an example of the Dragon range of voice dictation software. Its Vendor, Nuance, has discontinued the macOS version of its product. However, you can run a desktop-focused hypervisor- such as VMware Fusion or Parallels, which will enable you to run Windows in a VM, and give you access to that version of the software.
- Browse Securely: You can use a virtual machine for browsing. Doing so will enable you to visit sites without worrying about infection. You can take a snapshot of your device and then roll back to it after each browsing session. You can use type 2 desktop hypervisor to set up secure browsing. Alternatively, you can get a temporal virtual desktop located on the server.
Requirements of a modern data center
Because data centers contain so much expensive IT equipment, they have special requirements for security and power.
- Abundant, reliable power: The equipment in a data center often requires a large amount of power, from a source that is immune to interruptions through immediately available back-up power. Virtualized or software-defined data centers are more efficient and require much less power than traditional data centers.
- Cool conditions: All of the power and equipment in a data center generate a lot of heat, so data centers often require some kind of cooling equipment to operate optimally. Water can destroy computers, so sprinklers cannot be used to protect the equipment in a data center from fire. Instead, data centers can use chemical fire-retardant systems that smother flames without harming electronic equipment.
- Physical and virtual security measures: Security is an important aspect of any data center because of the business-critical applications and information it contains. A breach where sensitive customer or company data becomes exposed can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and, in worst-case scenarios, destroy a company’s brand and business. Both physical and virtual security measures are necessary to ensure that a data center stays secure and that businesses are not vulnerable to a data breach. A data center must be protected from theft with physical security measures such as locks, video surveillance, and restricted access. Network and application security software can provide essential virtual security measures.
Advantages and benefits of virtual machines
As compared to physical hardware, VMs offer several benefits that are worth a mention. Here are some of these benefits;
Resource utilization and Improved ROI
Because multiple VMs run on a single physical computer, customers will not have to buy a new server every time they want to run another operating system. This means they can get more returns from each piece of hardware they already own.
Scalability
With cloud computing, it is now easy to deploy multiple copies of the same virtual machine to serve better and increase your workload.
Portability
In terms of portability, VMs can be relocated as needed among the physical computers in a network. This makes it possible to allocate workloads to servers that have spare computing power.
Another benefit is that VMs can even move between on-premises and cloud environments. This makes them useful for hybrid cloud scenarios, in which you share computing resources between your data center and cloud provider.
Flexibility
Creating a virtual machine is faster and easier than installing an operating system on a physical server. This is because you can clone a virtual machine with an operating system already installed. Software testers and developers can create new environments on-demand to handle new tasks that arise.
Security
VMs improve Security in several ways compared to operating systems running directly on hardware.
A VM is a file that can be scanned for malicious software using an external program. You also need to ask your provider about the number of security layers they offer
You can create an entire snapshot of the VM at any point in time, then restore it to that state if it becomes infected with malware. This means you can effectively take the VM back in time. You can also completely delete a compromised VM and then recreate it quickly, to hasten recovery from malware infections.
How to Choose a Virtual Machine Provider?
Selecting a virtual machine and a cloud provider doesn’t have to be very challenging, as long as you know what you are looking for. A virtual machine you choose needs to fit your workload needs and business budget.
Aside from business budget and needs, other factors come into play. Below are a couple of critical elements you have to consider when selecting a virtual machine service provider.
Reliable support
Ensure there is a 24/7 customer support by email, phone, and chat. You want to communicate with a real person at the end of the helpline to take you through critical issues. It will be essential for you to note which cloud providers offer additional services for hands-on backing
Managed options
Ask yourself if the cloud provider provides both unmanaged and managed solutions. If they do not know about virtualization technology, consider going for a provider who is responsible for the whole setup, maintenance, and ongoing performance monitoring.
Software integration
Consider if your virtual machine environment will play well with others or not. You need one that can be seamlessly integrated with operating systems, open-source technology, third-party software, and other applications. These will help you deliver more solutions across your business.
You will need a virtual machine provider who has both support and strong partnership with the industry’s most used software suppliers.
High-quality network and infrastructure
How updated is the infrastructure your new virtual machine will run on? Consider aspects such as bare metal servers, modern data centers, and network backbone. A cloud provider should be able to deliver its part of the deal using high-standard hardware with high-speed networking technology.
Location
The closer the data is to your users, the less hassle you will run into with issues such as security, latency, and timely service delivery.
Backup and recovery
Find out any plans your cloud provider has in place for keeping your virtual machines up and running in case of unexpected events. Do they provide add-up backup and redundancy options for your virtualization environment? Ensure you can get a seamless operation in case of eventualities.
Seamless migration support
Your IT priorities will always evolve. Any virtual machine provider should be able to help you lift and shift between hybrid, on-premise, and off-premise environments. You need to look for full data ingest, over-the-network, and application-led migration options.
Scalability
How easy will it be for you to play around with your data center in terms of scaling up and down? You need to look for a virtual machine provider that delivers various configuration packages, be it for single or multi-tenant requirements.
Are you shopping for a data center or other Windows software products? SoftwareKeep is an industry leader in data center licensing and setup, and a trusted Microsoft Partner. We have a dedicated team of engineers who can get your data center set up and run in no time. Be sure to consult with us so that we can offer you a personalized and tailor-made solution that meets your needs.
Conclusion
As the Internet of Things expands, and the amount of data that is generated on a daily basis increases exponentially, the scalability and processing power of virtual data centers will become more and more critical. Data centers are increasingly important.
One more thing
We’re glad you’ve read this article upto here :) Thank you for reading.
If you have a second, please share this article on your socials; someone else may benefit too.
Subscribe to our newsletter and be the first to read our future articles, reviews, and blog post right in your email inbox. We also offer deals, promotions, and updates on our products and share them via email. You won’t miss one.
